The balance of payments is a systematic record of all economic transactions, including imports, exports, investments, and transfers, between the residents of one country and the residents of other countries over a specific period, typically a year. It consists of the current account, capital account, and financial account. The balance of payments provides insights into a country’s economic relationship with the rest of the world and its overall international financial position.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter which summarizes all articles from the previous week.
In international economics, the balance of payments (also known as balance of international payments and abbreviated BOP or BoP) of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time (e.g., a quarter or a year) and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services.
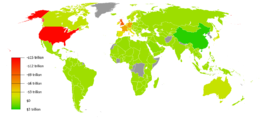
The balance of payments consists of two components: the current account and the capital account. The current account reflects a country's net income, while the capital account reflects the net change in ownership of national assets.
