The balance of trade refers to the difference between the value of a country’s exports and the value of its imports during a given period, usually a year. A positive balance of trade, or trade surplus, occurs when the value of exports exceeds the value of imports. A negative balance of trade, or trade deficit, occurs when the value of imports exceeds the value of exports. The balance of trade is an important component of the balance of payments and provides insights into a country’s trade performance and international competitiveness.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter which summarizes all articles from the previous week.
Balance of trade can be measured in terms of commercial balance, or net exports. Balance of trade is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance of trade for goods versus one for services. The balance of trade measures a flow variable of exports and imports over a given period of time. The notion of the balance of trade does not mean that exports and imports are "in balance" with each other.

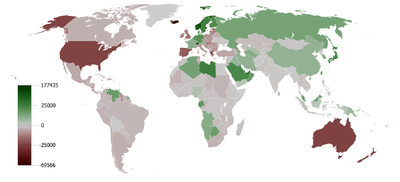
If a country exports a greater value than it imports, it has a trade surplus or positive trade balance, and conversely, if a country imports a greater value than it exports, it has a trade deficit or negative trade balance. As of 2016, about 60 out of 200 countries have a trade surplus. The notion that bilateral trade deficits are bad in and of themselves is overwhelmingly rejected by trade experts and economists.
